RMM For Uptime Monitoring: Complete Guide, Features and Details
In today’s hyper-connected world, downtime is more than just an inconvenience; it’s a potential disaster. For businesses of all sizes, consistent uptime is critical for maintaining productivity, ensuring customer satisfaction, and safeguarding revenue streams. But how do you proactively manage the uptime of your entire IT infrastructure, especially when dealing with a complex network of servers, workstations, and applications? That’s where Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) tools come into play, offering a centralized and automated approach to uptime monitoring.
RMM solutions provide a comprehensive suite of features designed to monitor, manage, and maintain IT infrastructure remotely. While they offer a wide range of functionalities, uptime monitoring is arguably one of their most vital capabilities. By continuously tracking the status of critical systems and applications, RMM tools can detect potential issues before they escalate into full-blown outages, allowing IT professionals to take proactive measures to prevent downtime and minimize its impact.

This article will delve into the world of RMM for uptime monitoring, exploring its core features, benefits, and practical considerations. We’ll examine how RMM tools work, what key metrics they track, and how they can be configured to meet the specific uptime monitoring needs of different organizations. Whether you’re a seasoned IT professional or just beginning to explore the world of RMM, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of how these powerful tools can help you achieve and maintain optimal uptime for your business.
Understanding RMM and Uptime Monitoring
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) is a software solution that allows IT service providers (MSPs) and internal IT departments to remotely monitor and manage client or company IT systems. It typically includes a suite of tools designed to automate tasks, detect and resolve issues, and improve overall IT efficiency. Uptime monitoring, in the context of RMM, refers to the continuous tracking of the availability and performance of servers, applications, network devices, and other critical IT infrastructure components.
Core Components of RMM for Uptime Monitoring
RMM platforms typically consist of several key components that work together to deliver comprehensive uptime monitoring capabilities:
- Agent Software: Small software programs installed on target devices (servers, workstations, etc.) that collect performance data and send it back to the RMM platform.
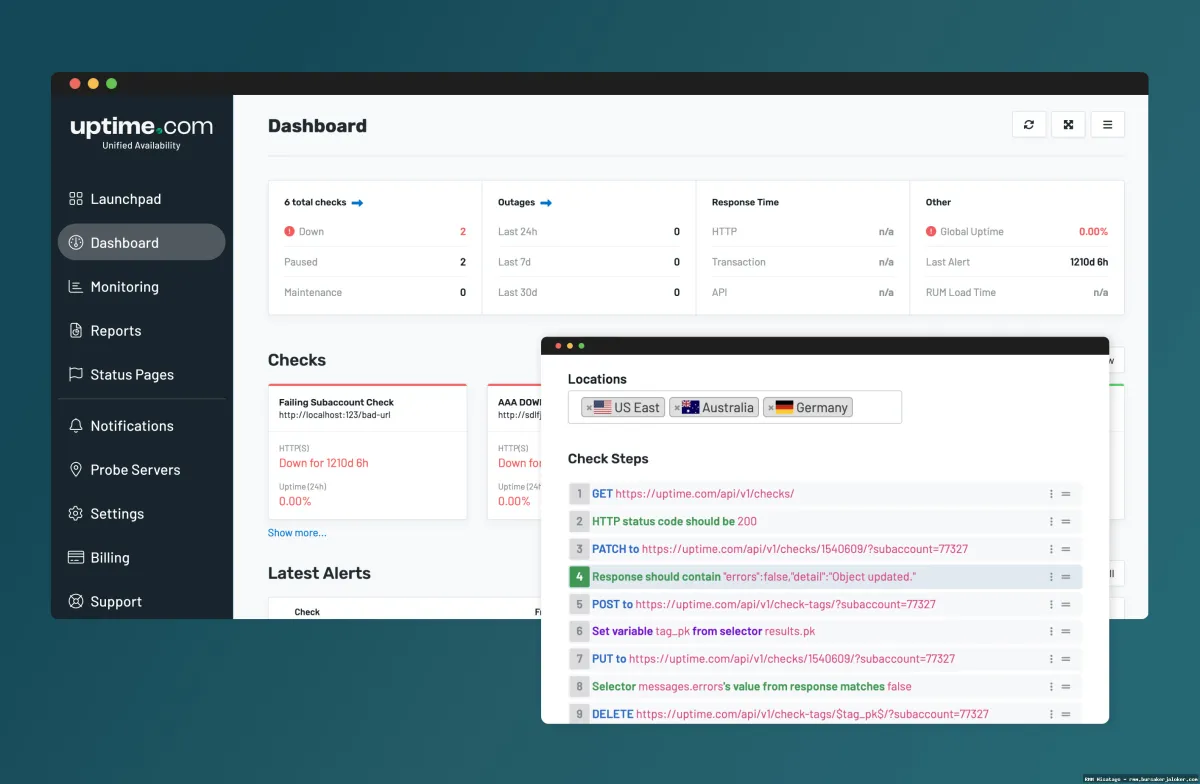
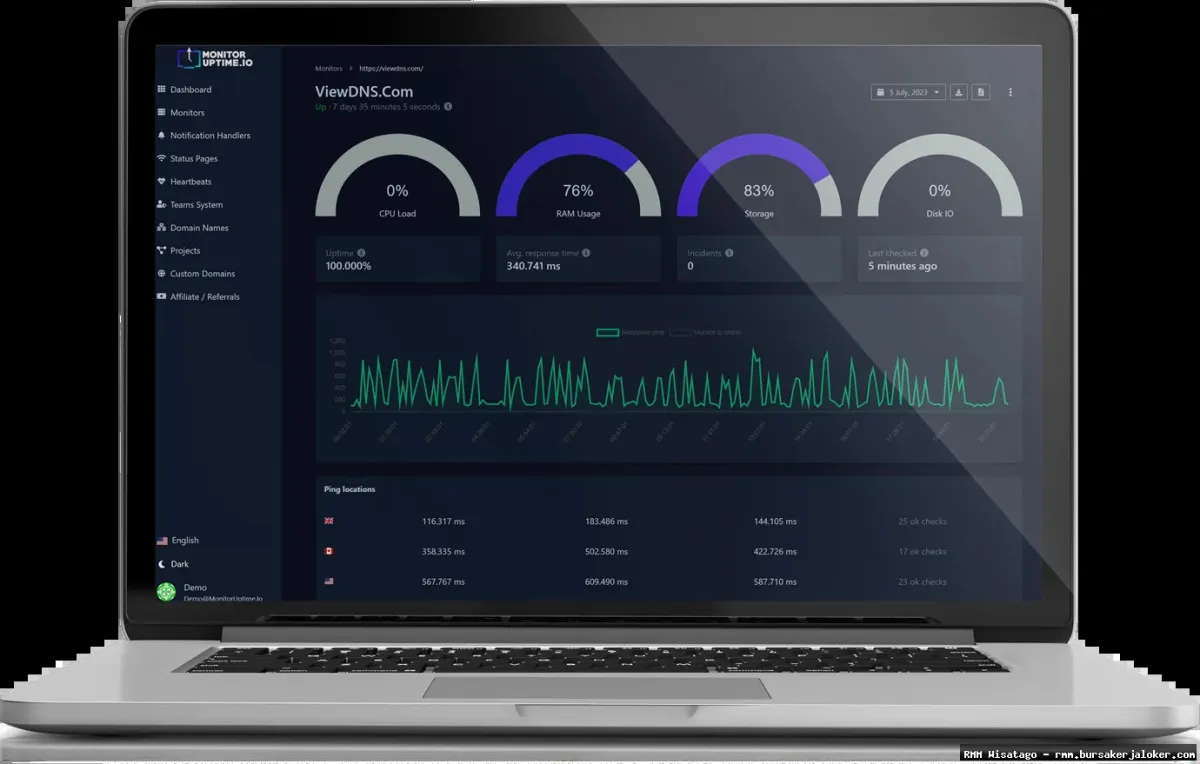
- Centralized Dashboard: A web-based interface that provides a single pane of glass view of the entire IT infrastructure, displaying the status of all monitored devices and applications.
- Alerting and Notification System: A system that generates alerts when pre-defined thresholds are exceeded or when specific events occur, notifying IT staff via email, SMS, or other channels.
- Reporting and Analytics: Tools for generating reports on uptime, performance, and other key metrics, providing insights into trends and potential problem areas.
- Automation Capabilities: Features that allow IT staff to automate routine tasks, such as patching, software deployment, and system maintenance, reducing the risk of human error and improving overall uptime.
Why is Uptime Monitoring Critical?
Uptime monitoring is essential for several reasons:
- Revenue Protection: Downtime can directly impact revenue, especially for businesses that rely on online sales or services.
- Customer Satisfaction: Frequent outages can erode customer trust and lead to churn.
- Productivity Enhancement: When systems are down, employees are unable to work, leading to lost productivity.
- Reputation Management: Publicized outages can damage a company’s reputation and brand image.
- Compliance Requirements: Some industries have strict uptime requirements to comply with regulations.
Key Features of RMM for Uptime Monitoring
A robust RMM solution offers a wide array of features specifically designed for comprehensive uptime monitoring:
Real-Time Monitoring
RMM tools provide real-time visibility into the status of all monitored devices and applications. This allows IT staff to quickly identify and respond to issues as they arise, minimizing the impact of downtime.
Threshold-Based Alerting
Administrators can configure alerts to be triggered when specific performance metrics, such as CPU utilization, memory usage, or disk space, exceed predefined thresholds. This proactive approach allows IT staff to address potential problems before they lead to outages.
Automated Remediation
Some RMM solutions offer automated remediation capabilities, allowing IT staff to configure automated responses to specific events. For example, if a server’s CPU utilization exceeds a certain threshold, the RMM tool can automatically restart the server or kill a runaway process.
Customizable Monitoring
The best RMM tools allow for customizable monitoring, enabling IT staff to track specific applications, services, and processes that are critical to their business. This ensures that all essential components are continuously monitored and protected. For more information, you can refer to ERP as an additional resource.
Remote Access and Control
RMM solutions provide secure remote access to managed devices, allowing IT staff to troubleshoot and resolve issues from anywhere with an internet connection. This is particularly valuable for organizations with geographically dispersed locations or remote employees.
Patch Management
Keeping systems up-to-date with the latest security patches is crucial for preventing vulnerabilities that could lead to downtime. RMM tools automate the patch management process, ensuring that all managed devices are protected against known threats.
Reporting and Analytics
RMM platforms generate detailed reports on uptime, performance, and other key metrics. These reports provide valuable insights into trends and potential problem areas, helping IT staff to proactively address issues and improve overall system stability.
Benefits of Using RMM for Uptime Monitoring
Implementing an RMM solution for uptime monitoring offers numerous benefits for businesses of all sizes:
Reduced Downtime
By proactively monitoring systems and applications, RMM tools can help to prevent downtime and minimize its impact when it does occur. This translates to increased productivity, improved customer satisfaction, and reduced revenue loss.
Improved IT Efficiency
RMM solutions automate many routine IT tasks, such as patching, software deployment, and system maintenance. This frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives, improving overall IT efficiency.
Enhanced Security
RMM tools help to improve security by ensuring that all managed devices are up-to-date with the latest security patches and by providing real-time visibility into potential security threats.
Proactive Problem Resolution
RMM tools enable IT staff to identify and resolve issues before they escalate into full-blown outages. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the impact of downtime and improve overall system stability.
Centralized Management
RMM platforms provide a centralized view of the entire IT infrastructure, making it easier to monitor, manage, and troubleshoot issues. This simplifies IT management and improves overall efficiency.
Cost Savings
By reducing downtime, improving IT efficiency, and enhancing security, RMM solutions can help to reduce overall IT costs. This makes RMM a valuable investment for businesses of all sizes.
Implementing RMM for Uptime Monitoring: Best Practices
To maximize the benefits of RMM for uptime monitoring, consider these best practices:
Define Clear Uptime Goals
Establish specific uptime goals for your critical systems and applications. This will help you to determine the appropriate monitoring thresholds and alerting configurations.
Prioritize Critical Systems
Focus your monitoring efforts on the systems and applications that are most critical to your business. This will ensure that you are proactively protecting your most valuable assets.
Configure Meaningful Alerts
Configure alerts that are meaningful and actionable. Avoid alert fatigue by only triggering alerts when there is a real problem that requires attention.
Automate Remediation Where Possible
Automate remediation tasks whenever possible to quickly resolve common issues and minimize downtime.
Regularly Review Reports and Analytics
Regularly review the reports and analytics generated by your RMM tool to identify trends and potential problem areas. This will help you to proactively address issues and improve overall system stability.
Provide Training to IT Staff
Ensure that your IT staff is properly trained on how to use the RMM tool and how to respond to alerts. This will enable them to effectively monitor and manage your IT infrastructure.
Choosing the Right RMM Solution
Selecting the right RMM solution is crucial for achieving optimal uptime monitoring. Consider the following factors when evaluating different RMM platforms:
Features and Functionality
Ensure that the RMM solution offers the features and functionality you need to monitor your specific IT infrastructure and meet your uptime goals. This includes real-time monitoring, threshold-based alerting, automated remediation, and customizable monitoring.
Scalability
Choose an RMM solution that can scale to meet your growing needs. This is particularly important for businesses that are expanding rapidly.
Integration
Select an RMM solution that integrates with your existing IT tools and systems. This will simplify IT management and improve overall efficiency.
Ease of Use
Choose an RMM solution that is easy to use and intuitive. This will reduce the learning curve for your IT staff and enable them to quickly become proficient with the tool.
Vendor Support
Select an RMM vendor that offers excellent customer support. This will ensure that you can get help when you need it.
Pricing
Compare the pricing of different RMM solutions and choose one that fits your budget. Consider the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing support costs.
Conclusion
RMM solutions provide a powerful and effective way to monitor and manage uptime, ensuring that critical systems and applications are always available. By implementing an RMM tool and following best practices, businesses can significantly reduce downtime, improve IT efficiency, enhance security, and reduce overall IT costs. In today’s competitive landscape, uptime is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity. Investing in an RMM solution for uptime monitoring is an investment in the success and resilience of your business.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about RMM for uptime monitoring
How can a Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) solution help proactively monitor server uptime and prevent downtime?
An RMM (Remote Monitoring and Management) solution plays a crucial role in proactively monitoring server uptime and minimizing downtime. It achieves this through several key mechanisms. Firstly, RMM tools provide real-time monitoring of servers, constantly tracking critical metrics like CPU usage, memory consumption, disk space, and network traffic. This allows for immediate detection of anomalies or performance degradation that could indicate an impending outage. Secondly, RMM systems often include automated alerting capabilities. When a predefined threshold is breached (e.g., CPU usage exceeding 80%), the RMM system automatically sends notifications to IT staff via email, SMS, or other channels. This enables quick intervention before a minor issue escalates into a full-blown server failure. Finally, RMM solutions facilitate remote access and remediation. IT technicians can remotely connect to the affected server, diagnose the problem, and implement fixes without needing to be physically present, significantly reducing response time and downtime.
What are the key uptime monitoring features to look for when selecting an RMM platform for my business?
When selecting an RMM platform for uptime monitoring, consider several key features. Firstly, ensure the RMM offers comprehensive monitoring capabilities, covering critical metrics like CPU utilization, memory usage, disk I/O, network performance, and application health. The ability to monitor various operating systems (Windows, Linux, macOS) and server types (physical, virtual, cloud-based) is also essential. Secondly, look for customizable alerting. The RMM should allow you to define thresholds and notification methods based on your specific needs and priorities. Consider features like escalation policies and alert suppression. Thirdly, remote access and control are vital for rapid response and remediation. The RMM should provide secure and reliable remote access to servers, allowing IT staff to diagnose and resolve issues from anywhere. Finally, reporting and analytics are crucial for identifying trends, predicting potential problems, and demonstrating the value of uptime monitoring. Look for features like historical data analysis, performance reports, and uptime guarantees.
Beyond basic server monitoring, what advanced uptime monitoring functionalities can an RMM provide, and how do they benefit my IT infrastructure?
Beyond basic server monitoring, RMM solutions offer advanced uptime monitoring functionalities that significantly benefit IT infrastructure. One key feature is application performance monitoring (APM), which tracks the performance of specific applications running on servers. This allows for identification of bottlenecks and optimization of application performance, leading to improved uptime. Another advanced functionality is synthetic monitoring, which simulates user interactions with applications and websites to proactively identify potential issues before they impact real users. RMMs often include network monitoring capabilities, tracking network devices, bandwidth usage, and network latency to ensure network stability and prevent network-related downtime. Furthermore, patch management capabilities within an RMM help maintain system security and stability by automatically deploying security patches and software updates, reducing the risk of vulnerabilities that could lead to downtime. These advanced functionalities collectively contribute to a more resilient and reliable IT infrastructure, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.