Remote Monitoring And Management Software: Complete Guide, Features and Details
In today’s complex IT landscape, businesses, especially Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and IT departments, face the daunting task of managing and maintaining numerous systems, devices, and networks. Keeping everything running smoothly, secure, and up-to-date is a constant challenge. This is where Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software comes into play, offering a centralized platform to streamline these critical operations.
RMM software provides a comprehensive suite of tools that enable IT professionals to proactively monitor the health and performance of IT assets, automate routine maintenance tasks, and remotely resolve issues before they escalate into major problems. By leveraging RMM, organizations can significantly improve their operational efficiency, reduce downtime, enhance security, and ultimately deliver better services to their clients or internal users.

This article will delve into the world of RMM software, exploring its key features, benefits, and considerations for choosing the right solution. Whether you’re an MSP looking to expand your service offerings or an IT manager seeking to optimize your department’s operations, understanding RMM is essential for navigating the modern IT management landscape. We’ll break down the complexities and provide a comprehensive guide to help you make informed decisions about implementing and utilizing RMM software effectively.
Remote Monitoring and Management Software: Complete Guide, Features and Details
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software is a platform used by IT professionals, particularly Managed Service Providers (MSPs), to remotely monitor, manage, and maintain their clients’ IT infrastructure. It provides a centralized view of all managed devices and systems, enabling proactive monitoring, automated maintenance, and rapid issue resolution. In essence, RMM helps keep IT environments healthy, secure, and optimized without requiring on-site visits for every minor problem.
What Problems Does RMM Solve?
RMM addresses several key challenges faced by IT departments and MSPs:
- Reactive Problem Solving: Without RMM, IT teams often react to problems after they occur, leading to downtime and user frustration. RMM enables proactive monitoring and issue resolution, preventing problems before they impact business operations.
- Inefficient Manual Maintenance: Manually patching systems, updating software, and performing other maintenance tasks is time-consuming and error-prone. RMM automates these tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
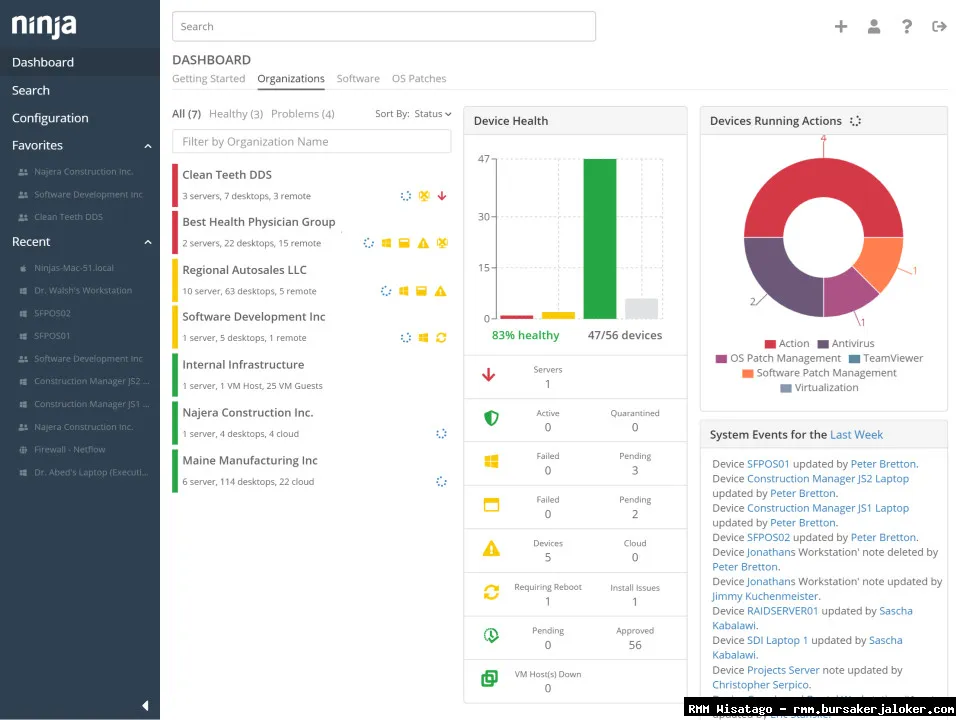
- Lack of Visibility: Without a centralized view of the IT environment, it’s difficult to identify potential problems or track the performance of systems. RMM provides a comprehensive dashboard that displays key metrics and alerts, giving IT teams the visibility they need to manage their infrastructure effectively.
- Security Vulnerabilities: Unpatched systems and outdated software are prime targets for cyberattacks. RMM helps ensure that all systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches, reducing the risk of breaches and data loss.
- Scalability Challenges: As businesses grow, managing their IT infrastructure becomes increasingly complex. RMM provides a scalable solution that can handle the needs of both small and large organizations.
Key Features of RMM Software
RMM software typically includes a wide range of features designed to streamline IT management and improve operational efficiency. Here are some of the most important features to look for:
Remote Monitoring
This is the core functionality of RMM software. It involves continuously monitoring the health and performance of managed devices and systems, including servers, workstations, network devices, and applications. Monitoring typically includes tracking metrics such as CPU utilization, memory usage, disk space, network traffic, and application availability. Alerts are generated when thresholds are exceeded, indicating potential problems.
Remote Access
RMM allows IT technicians to remotely access managed devices to troubleshoot issues, install software, and perform other tasks without needing to be physically present. Secure remote access is critical for quickly resolving problems and minimizing downtime. Look for features like unattended access, session recording, and multi-factor authentication.
Patch Management
Patch management automates the process of deploying software updates and security patches to managed devices. This helps ensure that all systems are up-to-date and protected against known vulnerabilities. RMM solutions often include features for scheduling patch deployments, testing patches before deployment, and reporting on patch status.
Automation
Automation is a key feature of RMM that allows IT teams to automate routine tasks, such as software installations, script executions, and system maintenance. This can significantly reduce the workload on IT staff and improve efficiency. Look for features like scripting capabilities, task scheduling, and pre-built automation templates.
Reporting and Analytics
RMM software provides detailed reports and analytics on the health and performance of managed devices and systems. This information can be used to identify trends, track performance improvements, and make informed decisions about IT infrastructure. Reports can include information on device uptime, patch compliance, security vulnerabilities, and resource utilization.
Alerting and Ticketing
When RMM detects an issue, it generates an alert and can automatically create a ticket in a ticketing system. This ensures that IT staff are notified of problems promptly and can begin working on a resolution. Look for features like customizable alert thresholds, ticket routing rules, and integration with popular ticketing systems.
Antivirus and Anti-Malware Integration
Many RMM solutions integrate with antivirus and anti-malware software to provide comprehensive security protection. This allows IT teams to monitor the status of antivirus software, deploy updates, and respond to security threats from a central console. Integration can include features like real-time threat detection, automated remediation, and reporting on security incidents.

Backup and Disaster Recovery
Some RMM solutions include backup and disaster recovery capabilities to protect data from loss due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks. This can include features like automated backups, cloud storage, and rapid recovery options. Ensuring data is backed up and recoverable is critical for business continuity.
Benefits of Using RMM Software
Implementing RMM software offers numerous benefits for both MSPs and internal IT departments:
- Increased Efficiency: Automating routine tasks and proactively resolving issues frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Reduced Downtime: Proactive monitoring and rapid issue resolution minimize downtime and improve system availability.
- Improved Security: Ensuring that all systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: Providing reliable and responsive IT support improves customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Scalability: RMM provides a scalable solution that can handle the needs of growing businesses.
- Centralized Management: RMM provides a single pane of glass for managing all IT assets, simplifying operations and improving visibility.
- Cost Savings: By reducing downtime, improving efficiency, and preventing security breaches, RMM can help organizations save money.
Choosing the Right RMM Software
Selecting the right RMM software is a critical decision that can significantly impact your IT operations. Here are some key factors to consider:
Your Specific Needs
Start by identifying your specific needs and requirements. What types of devices and systems do you need to monitor? What tasks do you want to automate? What security features are important to you? Consider your current infrastructure, future growth plans, and any industry-specific compliance requirements.
Features and Functionality
Evaluate the features and functionality of different RMM solutions to ensure they meet your needs. Do they offer the features you need, such as remote monitoring, remote access, patch management, automation, reporting, and security integration? Consider whether the features are easy to use and well-integrated.
Scalability
Choose an RMM solution that can scale to meet your future needs. Will it be able to handle your growing number of devices and users? Ensure the solution can accommodate your anticipated growth without requiring significant upgrades or changes.
Integration
Ensure that the RMM solution integrates with your existing IT systems, such as ticketing systems, antivirus software, and backup solutions. Seamless integration can streamline workflows and improve efficiency. Look for APIs and integrations that are well-documented and supported.
Pricing
Compare the pricing models of different RMM solutions. Some vendors charge per device, while others charge per user or offer tiered pricing plans. Consider the total cost of ownership, including software licenses, implementation fees, and ongoing maintenance costs. Understand the pricing structure and any potential hidden fees.
Vendor Reputation and Support
Research the vendor’s reputation and customer support. Read reviews and testimonials to see what other users have to say about their experience with the RMM solution. Ensure the vendor offers reliable support and documentation.
Ease of Use
Choose an RMM solution that is easy to use and intuitive. A complex and difficult-to-use solution will be less effective, even if it has all the features you need. Look for a user-friendly interface and comprehensive training materials.
Security
Security is paramount. Ensure the RMM solution is secure and protects your data from unauthorized access. Look for features like multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security audits.
Implementation and Best Practices
Once you’ve chosen an RMM solution, it’s important to implement it effectively to maximize its benefits. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Plan Your Implementation: Develop a detailed implementation plan that outlines your goals, timelines, and resources.
- Configure the Solution: Configure the RMM solution to meet your specific needs, including setting up monitoring thresholds, automation rules, and alerting policies.
- Train Your Staff: Provide adequate training to your IT staff on how to use the RMM solution effectively.
- Monitor Performance: Continuously monitor the performance of the RMM solution to ensure it is working as expected.
- Regularly Review and Update: Regularly review and update your RMM configuration to adapt to changing business needs and security threats.
- Document Everything: Maintain detailed documentation of your RMM configuration, policies, and procedures.
Conclusion
Remote Monitoring and Management (RMM) software is an indispensable tool for MSPs and IT departments looking to streamline their operations, improve security, and enhance service delivery. By proactively monitoring IT assets, automating routine tasks, and rapidly resolving issues, RMM helps organizations reduce downtime, improve efficiency, and deliver better services to their clients or internal users. Choosing the right RMM solution and implementing it effectively is critical for maximizing its benefits and achieving your IT management goals. By carefully considering your needs, evaluating different solutions, and following best practices, you can leverage RMM to transform your IT operations and drive business success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about remote monitoring and management software
What are the key benefits of using remote monitoring and management (RMM) software for my IT infrastructure?
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software offers numerous benefits for managing IT infrastructure. Firstly, it provides proactive monitoring of systems, networks, and applications, allowing you to identify and resolve issues before they cause significant downtime or impact end-users. This proactive approach saves time and money by preventing costly emergencies. Secondly, RMM tools automate routine tasks such as patch management, software updates, and security scans, freeing up IT staff to focus on strategic projects. Thirdly, remote access capabilities enable technicians to troubleshoot and resolve issues from anywhere, improving response times and reducing the need for on-site visits. Finally, comprehensive reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into IT performance, helping you optimize resource allocation and make data-driven decisions. In essence, RMM helps businesses improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance the overall reliability of their IT infrastructure. Implementing a new system can be a complex undertaking, ERP often requiring significant organizational change and careful planning
.
How does remote monitoring and management (RMM) software improve security for my business, and what security features should I look for?
Remote monitoring and management (RMM) software significantly enhances business security through several key features. One of the most important is automated patch management, ensuring that all systems are up-to-date with the latest security patches, mitigating vulnerabilities exploited by malware and cyberattacks. RMM platforms also offer remote access capabilities, allowing technicians to securely access and manage devices from anywhere, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Look for features like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to further secure remote sessions. Furthermore, RMM tools often include integrated security solutions, such as antivirus and anti-malware software, providing comprehensive protection against threats. Real-time monitoring and alerting can quickly detect suspicious activity, enabling rapid incident response. Finally, RMM platforms typically provide detailed security reports, helping you identify and address potential vulnerabilities in your IT infrastructure. A robust RMM solution with these features strengthens your security posture and protects your business from cyber threats.
What is the typical cost structure for remote monitoring and management (RMM) software, and what factors influence the pricing?
The cost structure for remote monitoring and management (RMM) software varies depending on several factors. The most common pricing model is a per-device or per-agent subscription, where you pay a monthly fee for each endpoint (e.g., computer, server, mobile device) managed by the software. Some vendors offer tiered pricing based on the number of devices or features required. Another model is all-inclusive pricing, which includes all features for a flat fee per device or user. Factors influencing pricing include the number of devices being managed, the specific features and functionalities included in the package (e.g., advanced security features, reporting capabilities), the level of support offered by the vendor, and the contract length. Some vendors may also offer discounts for longer-term contracts or larger deployments. Before choosing an RMM solution, it’s essential to carefully evaluate your business needs and compare pricing models to find the most cost-effective option. Consider the total cost of ownership, including implementation, training, and ongoing support, to make an informed decision.